前言:只记录自己需要的内容
辐射度量学

Radiant energy
能量,单位:J(Joule焦耳)
Radiant Flux
(单位时间能量 → 功率)单位:W(Watt),lm(lumen流明)
Intensity
the power per unit solid angle (立体角) $$ I(\omega) = \frac{\mathrm{d} \Phi}{\mathrm{d} \omega} $$
立体角
- 面积/半径^2,
$$ \Omega=\frac{A}{r^{2}} $$
- 单位:sr, steradians
$$ \mathrm{d} \omega=\frac{\mathrm{d} A}{r^{2}}=\sin \theta \mathrm{d} \theta \mathrm{d} \phi $$
方向性:用 w来表示方向
Irradiance
power per unit area $$ E(\mathbf{x}) \equiv \frac{\mathrm{d} \Phi(\mathbf{x})}{\mathrm{d} A} $$ 单位:W/m^2 | lm/m^2 = lux

irradiance解释衰减, 随着半径增大衰减越明显
Radiance
power per unit solid angle, per projected unit area.
$$
L(\mathrm{p}, \omega) \equiv \frac{\mathrm{d}^{2} \Phi(\mathrm{p}, \omega)}{\mathrm{d} \omega \mathrm{d} A \cos \theta}
$$
非垂直平面需要根据 θ 夹角计算

radiance 与intensity 和 irradiance 结合对比
Irradiance和Radiance之间的区别就在于是否有方向性
- Irradiance: power received by area dA 四面八方的光线积分起来
- Radiance: power received by area dA from “direction” dω
$$ \begin{aligned} d E(\mathrm{p}, \omega) &=L_{i}(\mathrm{p}, \omega) \cos \theta \mathrm{d} \omega \ E(\mathrm{p}) &=\int_{H^{2}} L_{i}(\mathrm{p}, \omega) \cos \theta \mathrm{d} \omega \end{aligned} $$
Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) 双向反射分布函数
理解
反射的理解:光线打到某个点,(被吸收了)然后反弹(发出)到其他地方

某个点从某个方向接受/向某个方向发射光线能量:radiance
- Differential irradiance incoming:
$$ d E\left(\omega_{i}\right)=L\left(\omega_{i}\right) \cos \theta_{i} d \omega_{i} $$
- Differential radiance exiting:
$$ d L_{r}\left(\omega_{r}\right) $$
通俗理解:这个微小面积接受的能量计算后,再分配到各个方向上
The Reflection Equation 反射方程
- 针对一个输出源(着色点),积分所有方向输入源(光照)的BRDF,获得最后的输出
$$ L_{r}\left(\mathrm{p}, \omega_{r}\right)=\int_{H^{2}} f_{r}\left(\mathrm{p}, \omega_{i} \rightarrow \omega_{r}\right) L_{i}\left(\mathrm{p}, \omega_{i}\right) \cos \theta_{i} \mathrm{d} \omega_{i} $$
The Rendering Equation 渲染方程
$$ L_{o}\left(p, \omega_{o}\right)=L_{e}\left(p, \omega_{o}\right)+\int_{\Omega^{+}} L_{i}\left(p, \omega_{i}\right) f_{r}\left(p, \omega_{i}, \omega_{o}\right)\left(n \cdot \omega_{i}\right) \mathrm{d} \omega_{i} $$

渲染方程考虑多个点光源:根据w方向加起来,同时考虑其他物体反射的光源。

一个神奇的抽象化理解:
- 光栅化的着色过程主要是直接光照(间接光照计算非常复杂)
- 全局光照:直接和间接光照的集合
- 会收敛到一个亮度
BRDF 材质
以前只有Blinn Phong的时候,通过非物理的方式模拟出各种材质。
Material == BRDF 决定光如何被反射
Diffuse / Lambertain Material

- 能量守恒:进出的irradiance相同(总量)
- 漫反射:出的radiance均匀→ $f_r = c$ (常量)
- 假设入射光和出射光都是均匀的→ $L_i = L_o$
- ρ: albedo(反射率, RGB)
Glossy Material(BRDF)
Ideal reflective / refractive material (BSDF * )
BSDF(散射) = BRDF(反射) + BTDF(折射)
Isotropic / Anisotropic Materials (BRDFs)
各向异性BRDF
Fresnel Reflection / Term (菲涅耳项)
和normal法线方向越接近,越少光被反射
- 近似:Schlick’s approximation
$$ \begin{aligned} R(\theta) &=R_{0}+\left(1-R_{0}\right)(1-\cos \theta)^{5} \ R_{0} &=\left(\frac{n_{1}-n_{2}}{n_{1}+n_{2}}\right)^{2} \end{aligned} $$
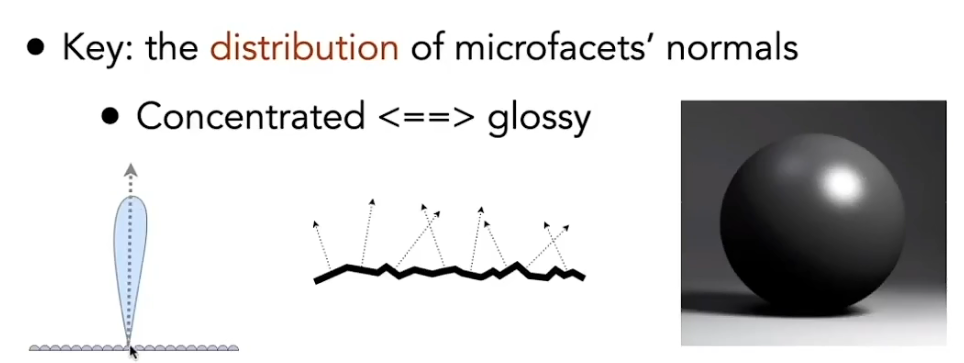
Microfacet Material 微表面材质
从足够远的地方看过去,无限接近镜面反射。但是不断拉近,表面会变得凹凸不平。

远处情况就是Glossy, 近处是diffuse,因此获得计算公式如下: $$ f(\mathbf{i}, \mathbf{o})=\frac{\mathbf{F}(\mathbf{i}, \mathbf{h}) \mathbf{G}(\mathbf{i}, \mathbf{o}, \mathbf{h}) \mathbf{D}(\mathbf{h})}{4(\mathbf{n}, \mathbf{i})(\mathbf{n}, \mathbf{o})} $$

- Fresnel term 表示菲尼尔效果
- shadowing-masking term 表示足够远的地方光滑但是细微的地方实际是凹凸不平产生遮挡阴影效果
- distribution of normals 表示凹凸不平的法线方向(细小平面的方向)
— 2023.2.10 更新 —